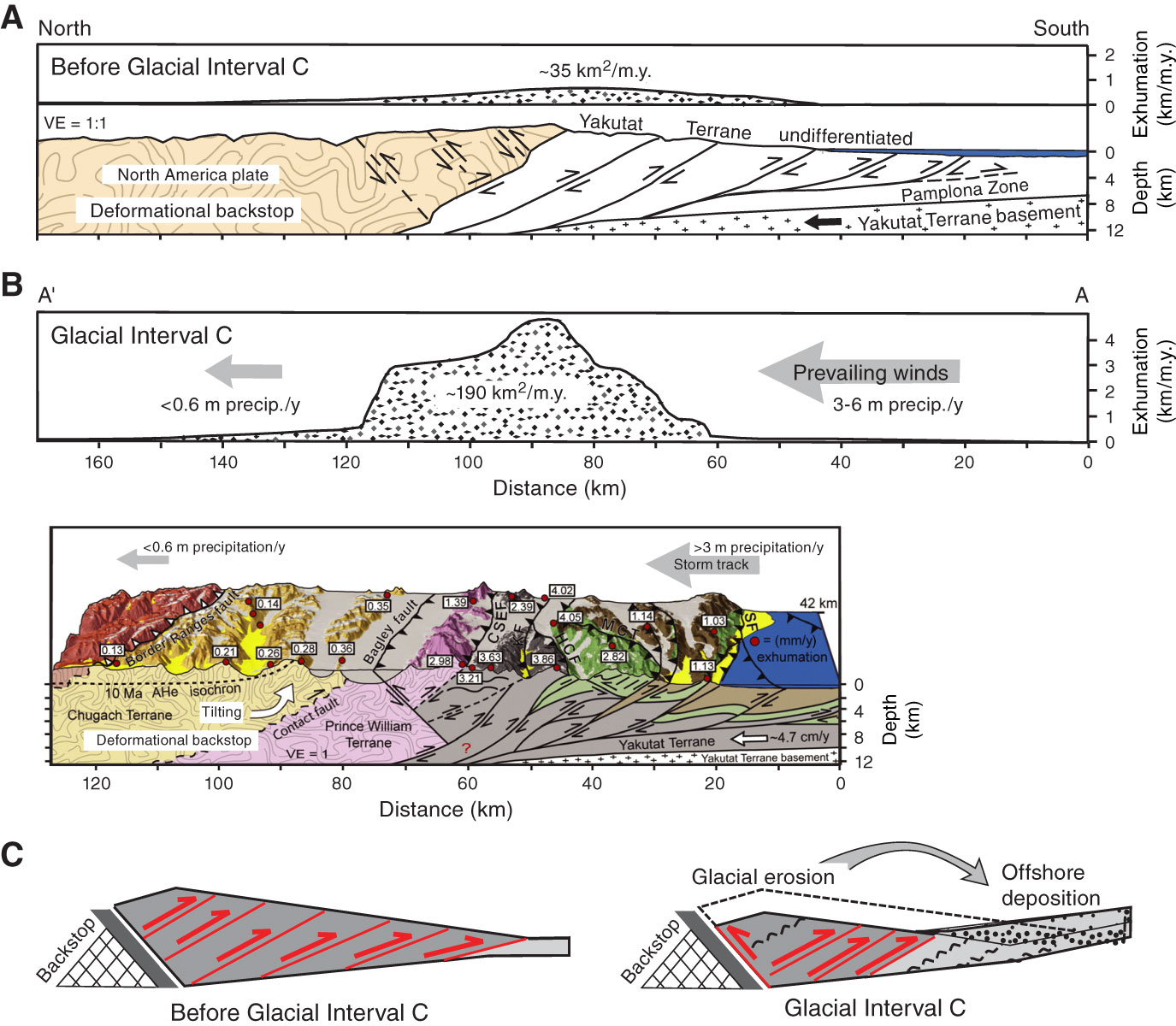
Figure F5. Proposed model of climate-related influences on orogen kinematics. Straight dashed lines depict structures with minor amounts of slip, and wavy dashed lines depict inactive structures. Strata along windward site: gray = Kultheith, green = Poul Creek, and brown = Yakataga Formations. A. Exhumational flux based on thermochronometry and architecture of the orogen prior to onset of Glacial Interval C at ~1 Ma, drawn along line A–A′ (Fig. F3) based on thermochronometry (Berger et al., 2008b; Spotila and Berger, 2010) and geologic data (Plafker et al., 1994; Bruhn et al., 2004). VE = vertical exaggeration. B. Exhumational flux based on thermochronometry and architecture of the orogen after the onset of Glacial Interval C. CSEF = Chugach-St. Elias Fault, KF = Kosakuts Fault, HCF = Hope Creek Fault, MCT = Miller Creek thrust fault, SF = Sullivan Fault, AHe = apatite (U-Th)/He. C. Interpretative model of the effect of glacial erosion and deposition on the St. Elias critical wedge. Before Glacial Interval C (left), the critical Coulomb wedge is wider and has greater relief. After the intensification of glaciation (right), increased glacial erosion and offshore deposition reduced relief, concentrated deformation, required enhanced back thrusting, and forced the termination of foreland structures, thereby narrowing the wedge. Modified from Berger et al. (2008a, 2008b).

Previous | Close | Next | Top of page